How did South African Apartheid happen, and how did it finally end? - Thula Simpson
TED-Ed
6 min, 52 sec
The video provides a detailed historical account of Apartheid in South Africa, its impact on the Black majority, and the eventual dismantling of the policy leading to Nelson Mandela's presidency.
Summary
- Apartheid imposed severe racial segregation and economic disparities on South Africa's Black majority.
- Student protests, such as the Soweto Uprising, and the efforts of leaders like Nelson Mandela and Steve Biko, were pivotal in fighting against the regime.
- International pressure and internal strife eventually led to the end of Apartheid, with Mandela becoming the first Black president in 1994.
- Despite the end of Apartheid, its legacy continues to affect South Africa, leaving many issues unresolved.
Chapter 1

The Soweto Uprising was a critical event in the fight against Apartheid, sparked by the imposition of Afrikaans in schools, leading to a brutal government response.
- On June 16, 1976, over 10,000 students protested against the enforcement of Afrikaans as a medium of instruction.
- The government responded with violence, resulting in over 150 student deaths.
- This event highlighted the oppressive nature of the Apartheid regime and galvanized further resistance.

Chapter 2
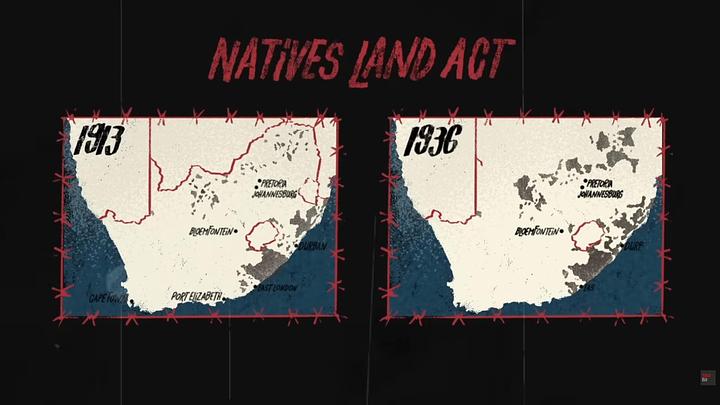
Apartheid's roots trace back to centuries of colonization and dispossession, leading to systemic segregation and economic exploitation of the Black population.
- Since the 1600s, Dutch and British settlers displaced local populations, leading to Black Africans living in overcrowded reserves.
- Black Africans migrated to white-controlled areas due to deprivation, only to be exploited for cheap labor.
- By the 20th century, 70% of the population lived on 13% of the land, leading to severe economic and spatial segregation.

Chapter 3

The National Party institutionalized Apartheid, leading to further racial segregation and the suppression of Black labor rights and political representation.
- The National Party won the 1948 elections and began forcibly relocating Africans to reserves, limiting their rights and movements.
- Apartheid policies included the abolition of mixed-race universities, anti-miscegenation laws, and the exclusion of non-whites from the voter rolls.
- The government brutally suppressed opposition, including the massacre at a PAC rally and the imprisonment of Nelson Mandela.

Chapter 4

Resistance to Apartheid persisted despite government oppression, leading to international condemnation and calls for the regime's end.
- Student activists, inspired by leaders like Steve Biko, continued to protest, leading to further government crackdowns.
- The killing of Biko and other activists sparked international outrage, resulting in trade embargoes against South Africa.
- Global pressure and internal conflicts forced the government to consider reforms and eventually led to the unbanning of the ANC.

Chapter 5

Apartheid ended with the election of Nelson Mandela as president, but the country continues to grapple with the policy's lasting impact.
- F.W. de Klerk's reforms and the release of Mandela paved the way for democratic elections and Mandela's presidency.
- Despite the end of Apartheid, South Africa still faces challenges in overcoming the deep-seated issues resulting from decades of racial segregation.

More TED-Ed summaries

Can you solve the sea monster riddle? - Dan Finkel
TED-Ed
A tale of the floating city of Atlantartica under siege by sea monsters, where the ruler must select the correct chest of pearls to appease them, using pattern recognition instead of understanding ancient numerals.

Can you outsmart the slippery slope fallacy? - Elizabeth Cox
TED-Ed
The video uses a historical context to challenge the validity of slippery slope arguments, illustrating how they can misrepresent the likelihood of extreme outcomes.

How to increase your happiness
TED-Ed
The video explores how gratefulness can lead to happiness, challenging the common belief that happiness breeds gratitude.

How to manage your emotions
TED-Ed
The video explores emotion regulation through the Process Model and its four steps, offering strategies for managing emotions and discussing the importance of balance in emotional well-being.